Inline classes是Value classes的子集,Value classes比Inline classes会得到更多优化,现阶段Value classes和Inline classes一样,只能在构造函数中传入一个参数,参数需要用val声明,将来可以在构造函数中添加多个参数,但是每个参数都需要用val声明。
声明一个内联类(value class)
声明一个内联类需要下面三个条件:
value class关键字@JvmInline注解- 主构造函数有且只能有一个属性
// For JVM backends
@JvmInline
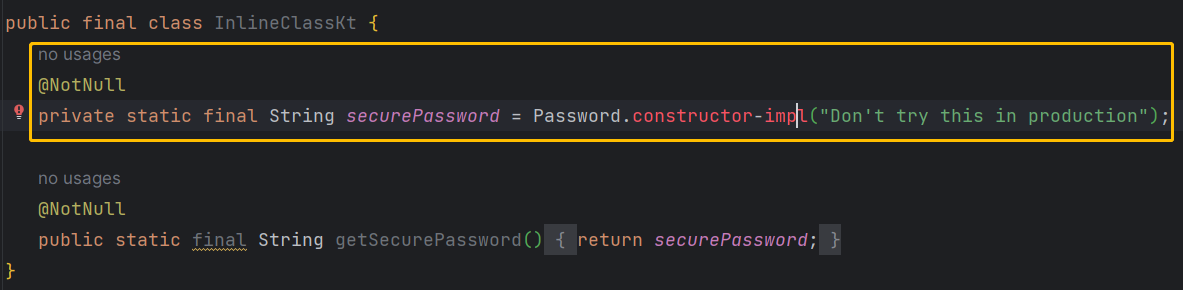
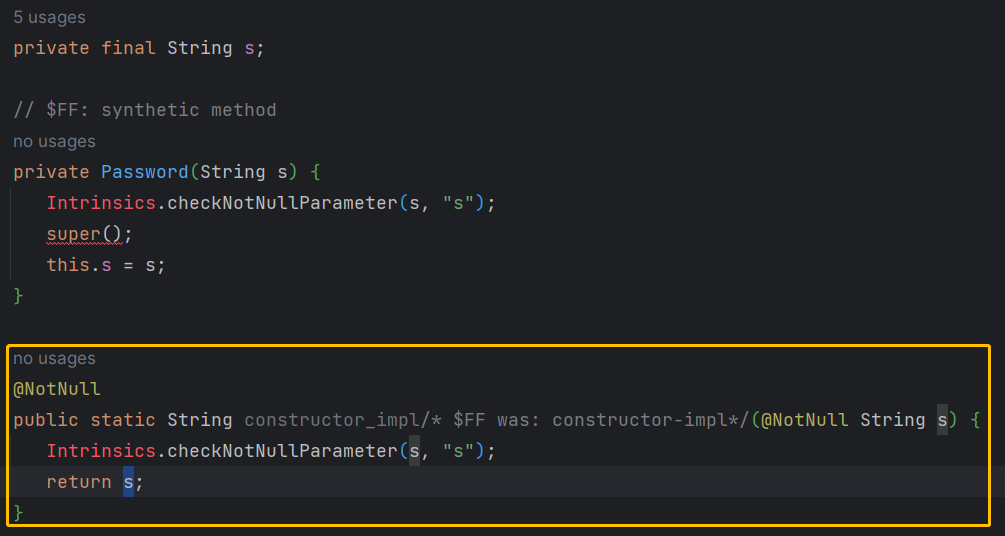
value class Password(private val s: String)
// No actual instantiation of class 'Password' happens
// At runtime 'securePassword' contains just 'String'
val securePassword = Password("Don't try this in production")
成员
value class允许声明属性(可计算属性、不支持幕后属性)或方法和init初始块。
@JvmInline
value class Name(val s: String){
init {
require(s.isNotEmpty())
}
val length : Int get() = s.length
fun greet(){
println("Hello, $s")
}
}
fun main() {
val name = Name("kotlin")
name.greet()
println(name.length)
}
继承
Value Class编译后将会添加fianl修饰符,因此不能被继承,同样也不能继承其他的类;但是可以实现接口。
interface Printable {
fun prettyPrint(): String
}
@JvmInline
value class Name(val s: String) : Printable {
override fun prettyPrint(): String = "Let's $s!"
}
表现形式
- Kotlin 编译器会用一个容器(wrapper)包装内联类。
- 在运行时内联类实体可以表现为包装类或者内联的具体类型。(Inline class instances can be represented at runtime either as wrappers or as the underlying type.)
- 正是因为内联类有两种表现形式,所以引用相等( === )会被禁止使用。(Because inline classes may be represented both as the underlying value and as a wrapper, referential equality is pointless for them and is therefore prohibited.)
- Kotlin 编译器会优先使用具体的类型来提高性能和优化代码,但有些场景将会保留包装类。(The Kotlin compiler will prefer using underlying types instead of wrappers to produce the most performant and optimized code. However, sometimes it is necessary to keep wrappers around.)
- 内联类在被用于其他类型的时候将表现为包装类。(As a rule of thumb, inline classes are boxed whenever they are used as another type.)
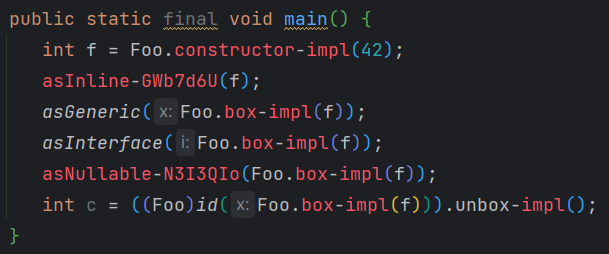
Foo和Foo?不是同样的类型,所以也表现为包装类。
interface I
@JvmInline
value class Foo(val i: Int) : I
fun asInline(f: Foo) {}
fun <T> asGeneric(x: T) {}
fun asInterface(i: I) {}
fun asNullable(i: Foo?) {}
fun <T> id(x: T): T = x
fun main() {
val f = Foo(42)
asInline(f) // unboxed: used as Foo itself
asGeneric(f) // boxed: used as generic type T
asInterface(f) // boxed: used as type I
asNullable(f) // boxed: used as Foo?, which is different from Foo
// below, 'f' first is boxed (while being passed to 'id') and then unboxed (when returned from 'id')
// In the end, 'c' contains unboxed representation (just '42'), as 'f'
val c = id(f)
}
破坏性?
- 编译器会将内联类编译成它们的内联属性,但由于内联属性和原有的属性相冲,出现错误。如
@JvmInline
value class UInt(val x: Int)
fun compute(x: Int) { }
fun compute(x: UInt) { }
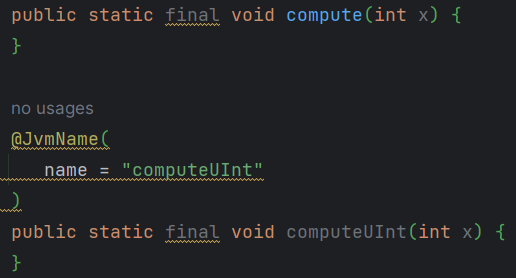
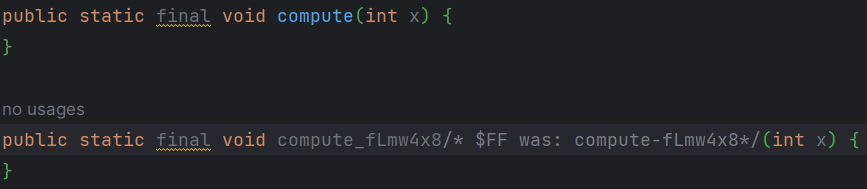
两个compute 方法将会在JVM平台编译成public final void compute(int x),出现相冲。
- 解决方法是:编译器将会把内联函数的方法名加上hashcode,形式是
public final void compute-<hashcode>(int x)。 - 因为这个破坏性,Java调用的时候不知道加的hashcode是什么,通过加
@JvmName注解给方法一个别名。
@JvmInline
value class UInt(val x: Int)
fun compute(x: Int) { }
@JvmName("computeUInt")
fun compute(x: UInt) { }